Devotee, December 18, 1973, Los Angeles: The scientists say that in the beginning the universe wasn’t created, and then all of a sudden there was a big explosion and everything just kind of happened. Everything just came into being.
Prabhupada: But how all of a sudden there can be explosion? What is this nonsense proposition? As soon as there is question of explosion, before the explosion takes place, there must be some arrangement. The time bomb explosion. So the bomb is prepared by something, some bomb is kept by somebody, and after some time it explodes. So how all of a sudden? Where does he get this idea? Just like if there is bomb explosion here, a child may think, “All of a sudden there is a bomb explosion”, but a sane man will not think that.
(Full Conversation)
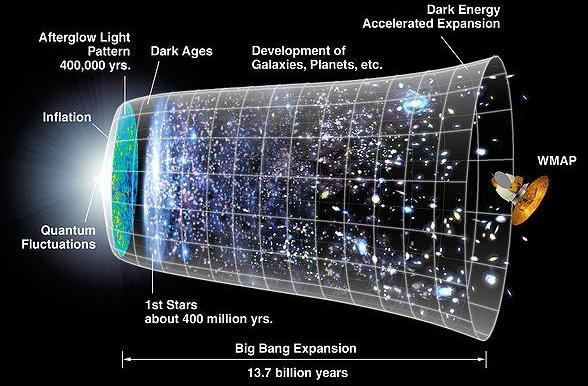
Illustration: Time Line of the Universe Credit: NASA/WMAP
“Revised Theory of Gravity doesn’t predict a Big Bang”
(PhysOrg.com) — By Lisa Zyga — The Big Bang theory has formed the basis of our understanding of the universe’s origins since it was first proposed in 1927 by Georges Lemaitre. And for good reason: the theory is supported by scientists’ latest observations and experiments, and is based on Einstein’s widely accepted theory of general relativity. But scientists are always on the lookout for any evidence that might suggest an alternative to the Big Bang. The latest in this area of research comes from astrophysicists Maximo Banados and Pedro Ferreira, who have resurrected a theory of gravity from the early 20th century and discovered that a modified version of the theory may hold some surprises.
In a recent study published in Physical Review Letters, Banados and Ferreira have reconsidered the theory of gravity proposed by Arthur Eddington, a contemporary of Einstein. Eddington is perhaps best known for his trip to the Island of Principe on the west coast of Africa in 1919, where during a solar eclipse he observed that the Sun’s gravity does indeed bend starlight, providing one of the earliest confirmations of general relativity.
Although Eddington played a significant role in developing general relativity, during the following decades he became more interested in finding a theory to unify gravity and quantum mechanics – a task that is still being studied today. In 1924, Eddington proposed a new “gravitational action” as an alternative to the Einstein-Hilbert action, which could serve as an alternative starting point to general relativity.
In astrophysics, a gravitational action is the mechanism that describes how gravity can emerge from space-time being curved by matter and energy. However, Eddington’s theory of gravity only worked for empty space and didn’t include any source of energy such as matter, making it an incomplete theory.
Since Eddington’s proposal, scientists have attempted various ways of including matter into the theory, although they have run into problems. In this study, Banados and Ferreira have tried a new way to extend the theory to include matter by using a gravitational action called the Born-Infeld action.
In their analysis, the scientists found that a key characteristic of Eddington’s revised theory of gravity is that it reproduces Einstein gravity precisely in the vacuum conditions (with no matter), but it produces new effects when matter is added. Due to this characteristic, the revised theory has implications especially for high-density regions, such as in the very early Universe or within a black hole. For instance, the theory predicts a maximum density of homogeneous and isotropic space-time, which could have implications for black hole formation.
More intriguingly, the theory could lead to an entirely new view of the Universe that doesn’t include a Big Bang. In Big Bang theory, the state of the Universe is a singularity in early times, meaning that the Universe was once infinitely small. However, Eddington’s revised theory requires a minimum length of space-time at early times, which means that the Universe could not have been a singularity.
The theory predicts that, depending on the Universe’s initial density, it may have loitered for a long time at a relatively small size before growing large enough to be controlled by standard cosmological evolution.
Another possibility, depending on the initial conditions, is that the Universe could have undergone a bounce, resulting from the collapse of a previous Universe. Any kind of singularity-free Universe would solve the singularity problem that has bothered scientists about general relativity, since a singularity cannot be mathematically defined.
“Taking as a starting point what is a very old idea, we have ended up with a theory that has this very interesting property of not having singularities,” Ferreira, a professor of astrophysics at the University of Oxford, told PhysOrg.com. “It was unexpected and definitely not what we were looking for.”
In the future, Banados and Ferreira hope to perform a more detailed analysis of the gravitational Born-Infeld action. While the current study only looks at the classical behavior of the theory, there could also be quantum behavior, such as with the bounce concept. In addition, the scientists plan to look at the possible effects of a cosmological constant, which they did not investigate here. However, they note that the theory is still in the early conceptual stages, and has a long way to go before they know how accurate it is.
“The alternatives to Einstein’s theory are all hypothetical possibilities,” Ferreira said. “The goal is to try and find some key observational test that may distinguish between Einstein’s theory and the one we have stumbled upon.”







Speak Your Mind